Step into the world of Understanding mutual funds where the magic of investing comes alive. Get ready to dive deep into the realm of financial possibilities, exploring the ins and outs of mutual funds in a whole new light.
As we unravel the mysteries behind mutual funds, you’ll discover a treasure trove of knowledge waiting to be explored.
What Are Mutual Funds?
Mutual funds are investment vehicles that pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities, such as stocks, bonds, or other assets. These funds are managed by professional fund managers who make investment decisions on behalf of the investors.
Types of Mutual Funds
- Equity Funds: These mutual funds invest primarily in stocks, offering potential for high returns but also higher risk.
- Debt Funds: Debt funds invest in fixed-income securities like bonds and provide regular income with lower risk compared to equity funds.
- Balanced Funds: These funds invest in a mix of stocks and bonds to provide a balanced approach to risk and return.
- Index Funds: Index funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500, by holding the same securities in the same proportion as the index.
Benefits of Mutual Funds
Investing in mutual funds offers several advantages compared to individual stock picking:
- Diversification: Mutual funds provide instant diversification by investing in a variety of securities, reducing overall risk.
- Professional Management: Fund managers handle the day-to-day investment decisions, leveraging their expertise for better returns.
- Liquidity: Mutual funds offer liquidity as investors can easily buy or sell fund shares at the prevailing net asset value (NAV).
- Cost-Effective: Investing in mutual funds is cost-effective as the expenses are shared among all investors, making it a more affordable option.
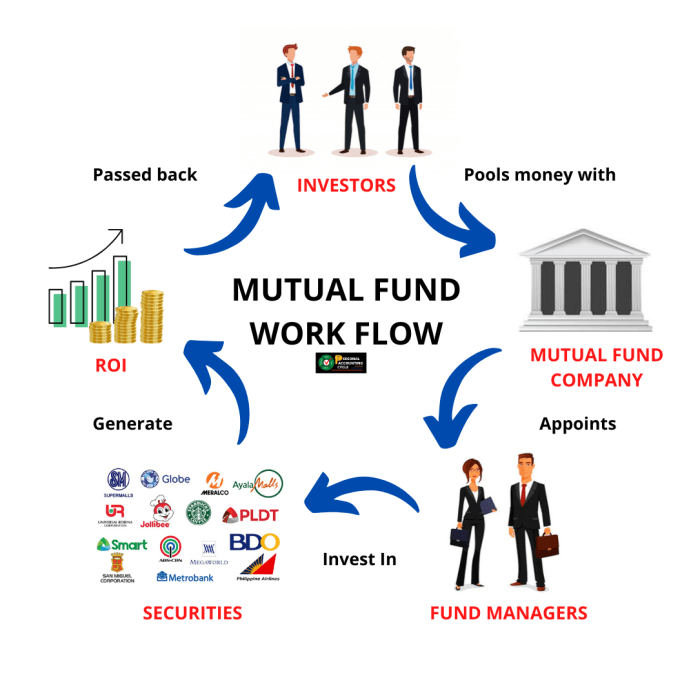
How Do Mutual Funds Work?
When it comes to mutual funds, understanding how they work is crucial for investors looking to grow their money. Let’s dive into the details to shed some light on the inner workings of mutual funds.
Buying and Selling Mutual Fund Units
When investors buy mutual fund units, they are essentially pooling their money with other investors to create a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. The fund manager then uses this pool of money to make investments on behalf of the investors. Selling mutual fund units involves redeeming them back to the fund, which can typically be done on a daily basis.
Role of a Fund Manager
The fund manager plays a key role in managing the fund’s investments. They are responsible for researching, selecting, and monitoring the securities within the fund’s portfolio. Fund managers aim to achieve the fund’s investment objectives and maximize returns for investors while managing risks.
Net Asset Value (NAV) Calculation
The Net Asset Value (NAV) of a mutual fund is calculated by subtracting the fund’s liabilities from its assets and dividing the result by the number of outstanding units. NAV represents the per-unit value of the fund and is calculated at the end of each trading day. A higher NAV does not necessarily mean a better-performing fund.
Generating and Distributing Mutual Fund Returns
Mutual fund returns are generated through a combination of capital gains, dividends, and interest earned on the securities held in the fund’s portfolio. These returns are then distributed to investors in the form of dividends or reinvested back into the fund to increase its NAV. It’s important for investors to understand how returns are generated and distributed to make informed investment decisions.
Types of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds come in various types, each with its own unique characteristics and investment strategies. Let’s delve into the different types of mutual funds to understand how they operate and what sets them apart.
Open-End vs. Closed-End Mutual Funds
Open-end mutual funds are continuously issued and redeemed based on demand at the net asset value (NAV) per share. Closed-end mutual funds, on the other hand, have a fixed number of shares that are traded on exchanges like stocks.
Actively Managed vs. Passively Managed Funds
Actively managed funds involve fund managers making investment decisions in an attempt to outperform the market. Passively managed funds, such as index funds, aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index.
Risk Profiles of Different Mutual Funds
Actively managed funds typically carry higher fees due to the active management involved, which can impact returns. Passively managed funds tend to have lower fees but also lower potential for outperformance.
Specialty Funds
Specialty funds focus on specific sectors, themes, or social responsibility criteria. Sector-specific funds invest in a particular industry, thematic funds target specific trends or concepts, and socially responsible funds consider environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors in their investment decisions.
Benefits and Risks of Investing in Mutual Funds
Investing in mutual funds offers a range of benefits, but it also comes with certain risks that investors need to be aware of.
Advantages of Diversification through Mutual Funds
Diversification is a key benefit of investing in mutual funds. By pooling money from multiple investors, mutual funds spread investments across a variety of securities such as stocks, bonds, and other assets. This diversification helps reduce the overall risk in a portfolio, as losses in one investment can be offset by gains in another.
Risks Involved in Investing in Mutual Funds
While diversification helps mitigate risk, investing in mutual funds still carries certain risks. Market risk is one of the primary risks, as the value of investments in the fund can fluctuate due to market conditions. Liquidity risk is another concern, as some mutual funds may have restrictions on when investors can redeem their shares.
Professional Management Offered by Mutual Funds
One of the advantages of mutual funds is that they offer professional management to investors. Fund managers make investment decisions on behalf of the investors, based on their expertise and research. This can be beneficial for investors who may not have the time or knowledge to manage their own investments.
Tax Implications of Investing in Mutual Funds
Investing in mutual funds can have tax implications for investors. Depending on the type of fund and the holding period, investors may be subject to capital gains taxes when they sell their shares. It’s important for investors to understand the tax implications of investing in mutual funds and consult with a tax advisor if needed.
How to Choose a Mutual Fund
When it comes to choosing a mutual fund, there are several important factors to consider. From your investment goals to the fund’s performance history, each aspect plays a crucial role in making the right decision.
Investment Goals, Risk Tolerance, and Expenses
- Before selecting a mutual fund, it’s essential to define your investment goals and risk tolerance. Whether you’re looking for long-term growth or stable income, aligning your goals with the fund’s objectives is key.
- Consider the expenses associated with the mutual fund, including management fees, sales charges, and other costs. A high expense ratio can eat into your returns over time, so opt for funds with lower fees.
Researching Fund Performance History
- Researching the fund’s performance history is crucial in determining its potential for growth. Look at how the fund has performed in different market conditions and compare it to its benchmark index.
- Consider factors such as the fund manager’s track record, investment strategy, and consistency in delivering returns. Past performance doesn’t guarantee future results, but it can provide valuable insights.
Importance of Expense Ratios and Fees
- Expense ratios and fees can significantly impact your overall returns. A lower expense ratio means more of your money is invested rather than being paid out in fees. Compare expense ratios across different funds to make an informed decision.
- Be aware of other fees such as front-end and back-end loads, redemption fees, and 12b-1 fees. These additional costs can reduce your returns, so factor them into your decision-making process.
Building a Diversified Mutual Fund Portfolio
- Diversification is key to managing risk in your investment portfolio. Spread your investments across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions to reduce the impact of market fluctuations on your overall returns.
- Consider investing in a mix of mutual funds with varying risk profiles, such as equity funds, bond funds, and index funds. This diversification can help balance out your portfolio and optimize returns.
Mutual Funds vs. Other Investment Options
When considering investment options, it’s important to weigh the pros and cons of mutual funds compared to alternatives like stocks, bonds, and ETFs. Each type of investment has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, so understanding how mutual funds stack up against other options is crucial for making informed decisions about your finances.
Comparing Mutual Funds with Stocks, Bonds, and ETFs
- Mutual Funds: Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other securities. They are managed by professional fund managers, offering diversification and professional expertise.
- Stocks: Investing in individual stocks means buying shares of a specific company. Stocks can offer high returns but come with higher risk due to the volatility of individual companies.
- Bonds: Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations. They provide fixed income but may offer lower returns compared to stocks. Bonds are considered less risky than stocks.
- ETFs: Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are similar to mutual funds but trade on stock exchanges like individual stocks. They offer diversification and flexibility but may have higher trading costs.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Mutual Funds
- Advantages:
- Professional Management: Mutual funds are managed by professionals who make investment decisions on behalf of investors.
- Diversification: Mutual funds offer a diversified portfolio, reducing risk compared to investing in individual securities.
- Liquidity: Mutual funds provide easy access to your money, allowing you to buy or sell shares on any business day.
- Disadvantages:
- Fees: Mutual funds charge management fees and expenses, which can eat into your returns over time.
- Limited Control: Investors have limited control over the specific securities within the fund’s portfolio.
- Market Risk: Mutual funds are subject to market fluctuations, and the value of your investment can go up or down.
When Investing in Mutual Funds Makes Sense
- Long-Term Investing: Mutual funds are ideal for long-term investors looking to build wealth gradually over time.
- Diversification: If you want a diversified portfolio without the hassle of managing individual investments, mutual funds can be a convenient option.
- Access to Expertise: For those who lack the time or expertise to research and manage investments, mutual funds provide access to professional fund managers.
