Get ready to dive into the world of dollar-cost averaging, a savvy investment strategy that can help you navigate the ups and downs of the market with finesse. Buckle up as we break down the basics, benefits, and implementation steps of this financial technique that’s got everyone talking.
Definition and Basics
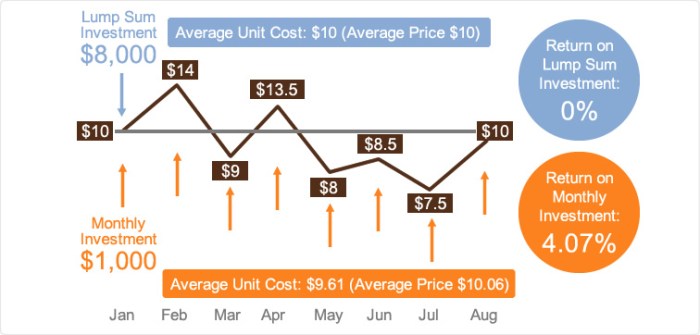
Dollar-cost averaging is an investment strategy where an individual invests a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions. This approach aims to reduce the impact of market volatility by spreading out the investment over time.
How Dollar-Cost Averaging Works
Dollar-cost averaging works by consistently investing a fixed amount of money on a scheduled basis, such as monthly or quarterly. This strategy allows investors to buy more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high. Over time, this can potentially lower the average cost per share.
- By investing a fixed amount regularly, investors can take advantage of market fluctuations without trying to time the market.
- As the market goes through ups and downs, dollar-cost averaging can help smooth out the overall purchase price of investments.
- Over the long term, this strategy can help reduce the risk of making large investments at the wrong time.
Examples of Dollar-Cost Averaging Implementation
- Investor A decides to invest $500 in a particular stock every month, regardless of the stock price. This consistent approach allows Investor A to accumulate more shares when the stock price is low and fewer shares when the price is high.
- Company B offers a 401(k) plan where employees automatically contribute a portion of their paycheck to a diversified portfolio. This automatic investment strategy follows the principles of dollar-cost averaging.
- Student C sets up a recurring investment plan where a fixed amount is automatically deducted from their bank account and invested in a low-cost index fund. This hands-off approach aligns with the dollar-cost averaging strategy.
Benefits
Using dollar-cost averaging comes with several advantages that can help investors navigate the ups and downs of the market.
Reducing Market Volatility Impact
Dollar-cost averaging helps reduce the impact of market volatility by spreading out investments over time. This strategy allows investors to buy more shares when prices are low and fewer shares when prices are high, ultimately averaging out the cost per share.
Potential Long-Term Benefits
Compared to lump-sum investing, dollar-cost averaging can provide potential long-term benefits. By consistently investing a fixed amount over time, investors can benefit from the power of compounding returns. This approach also helps to mitigate the risk of investing a large sum at an inopportune time, as the investments are spread out.
Implementation
When setting up a dollar-cost averaging strategy, there are several key steps to follow to ensure its success. This method involves investing a fixed amount of money at regular intervals, regardless of market conditions, to reduce the impact of market volatility on your investments.
Setting Up a Dollar-Cost Averaging Strategy
- Choose an investment platform or brokerage account that allows for recurring investments.
- Determine the frequency of your investments, whether it’s weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly.
- Select the investment options you want to include in your dollar-cost averaging plan.
- Set up automatic transfers or contributions to fund your investments regularly.
Choosing Investment Options
- Consider a mix of assets such as stocks, bonds, index funds, or ETFs to diversify your portfolio.
- Research and select investments that align with your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment timeline.
- Review and adjust your investment options periodically to ensure they continue to meet your objectives.
Adjusting Your Plan Over Time
- Monitor the performance of your investments and make adjustments as needed based on market conditions and your financial situation.
- Reassess your investment goals and risk tolerance regularly to make sure your dollar-cost averaging strategy remains relevant.
- Consider increasing or decreasing your investment amounts based on changes in your income or financial goals.
Considerations
When it comes to dollar-cost averaging, there are some important factors to consider before diving in.
Potential Drawbacks
While dollar-cost averaging can help reduce the impact of market volatility, it may also limit potential gains in a rapidly rising market.
It’s important to remember that this strategy involves consistent, fixed investments regardless of market conditions, which can sometimes lead to missed opportunities for higher returns.
Comparison with Lump-Sum Investing
Comparing dollar-cost averaging with lump-sum investing can provide insights into the pros and cons of each approach.
- Dollar-Cost Averaging: In a volatile market, this strategy can help mitigate risk by spreading out investments over time.
- Lump-Sum Investing: With a lump-sum approach, investors have the potential to benefit from immediate market gains, but also face higher risk if the market declines shortly after investing.
Common Misconceptions
There are some myths surrounding dollar-cost averaging that are important to address.
- Myth: Dollar-cost averaging guarantees profits in any market.
- Reality: While this strategy can help manage risk, it does not guarantee profits and is not foolproof against market downturns.
- Myth: Dollar-cost averaging is always the best approach for long-term investing.
- Reality: The effectiveness of dollar-cost averaging depends on individual circumstances and market conditions, and there may be situations where lump-sum investing is more suitable.
